
Blood is the lifeline of the human body, carrying vital nutrients, oxygen, and waste products throughout the system. Keeping track of the health of your blood can reveal a lot about your overall health. One of the most common and essential tools to assess your blood’s health is the Complete Blood Count (CBC) test.
But what exactly is this scan – and why is it so important? 🤔
A CBC blood test is a broad diagnostic tool healthcare providers use to evaluate your overall health and detect a wide range of disorders, such as anemia, infection, and even certain cancers. It’s a fundamental part of routine medical checkups, providing crucial information about the components of your blood.
This guide aims to demystify the CBC test for non-physicians 🤓, giving you a clearer understanding of what it measures, how to interpret the results, and when and why you might need it. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of how this blood test works and why it’s one of the most frequently ordered tests in medical practice.
And if you’re already familiar with the basics and want to get quick to scheduling, sign up here:
A CBC blood test provides a comprehensive snapshot of your blood health by measuring different blood components. These components are essential for various functions like carrying oxygen, fighting infections, and clotting.
Let’s break down each of these components to understand what the CBC test is measuring.
Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and returning carbon dioxide for exhalation. A CBC test measures the number of RBCs, which can indicate conditions such as anemia or dehydration.
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
White blood cells help fight infection. The CBC test checks WBC levels, which can point to infections, inflammation, or immune disorders if the count is too high or too low.
Platelets
Platelets play a crucial role in blood clotting. Low platelet levels can lead to excessive bleeding, while high levels can increase the risk of clotting disorders.
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the protein in RBCs that carries oxygen. Abnormal levels can indicate issues like anemia, especially if they deviate from the norm.
Hematocrit
This is the proportion of your blood that is made up of RBCs. A low hematocrit may suggest anemia, while a high hematocrit could indicate dehydration or other conditions.
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
MCV measures the average size of red blood cells. Abnormal sizes can indicate different types of anemia (e.g., microcytic anemia for smaller cells and macrocytic anemia for larger cells).
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH)
MCH measures the average amount of hemoglobin in each red blood cell. Low MCH levels can indicate iron-deficiency anemia, while high levels may suggest vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC)
MCHC represents the concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells. A low MCHC level is often found in iron deficiency anemia, while a high level could suggest hereditary spherocytosis.
Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW)
RDW shows the variation in the size of your red blood cells. High RDW values may indicate an increased risk of anemia or other blood disorders.
Platelet Count
This measures the number of platelets in your blood. Both high and low platelet counts can indicate various health issues, such as thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) or thrombocytosis (high platelet count).
Mean Platelet Volume (MPV)
MPV provides insight into the average size of your platelets. Larger platelets might indicate faster platelet turnover, which can be seen in conditions like bone marrow disorders.
Platelet Distribution Width (PDW)
PDW measures the variation in platelet size. It can help identify disorders that affect platelet production or destruction.
Beyond just the total count, the CBC also provides a breakdown of different types of white blood cells:

Understanding the normal ranges for each component of the CBC test is crucial, as deviations could indicate health concerns. However, normal ranges can vary by age, gender, and even altitude.
Normal ranges are generally well-defined for RBCs, WBCs, platelets, and other components in adults.
| Parameter | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.3 – 17.2 | 12.0 – 15.0 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 38.9 – 50.9 | 34.8 – 45.0 |
| White Blood Cells (WBC) (10^9/L) | 4.5 – 11.0 | 4.5 – 11.0 |
| Platelets (10^9/L) | 150 – 450 | 150 – 450 |
| Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) (fL) | 83.3 – 98.0 | 83.3 – 98.0 |
These ranges can differ significantly, with infants typically having higher red blood cell counts at birth and these values gradually declining as they grow.
| Parameter | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.7 – 17.1 | 10.7 – 17.1 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 33 – 54 | 33 – 54 |
| WBC (10^9/L) | 5.0 – 15.5 | 5.0 – 15.5 |
| Platelets (10^9/L) | 150 – 450 | 150 – 450 |
| Parameter | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.0 – 14.3 | 11.3 – 14.3 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 31 – 41 | 32 – 41 |
| WBC (10^9/L) | 4.5 – 11.0 | 4.5 – 11.0 |
| Platelets (10^9/L) | 150 – 450 | 150 – 450 |
Several factors, such as pregnancy, high altitude, recent physical activity, and certain medications, can temporarily skew CBC results.
Your “normal” may be different from someone else’s based on your health, medical history, and individual physiology. It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider to interpret the results in the context of your health.
The CBC blood test is versatile and can be used in various scenarios. Here are the most common reasons for getting a CBC blood test:
It is often part of an annual health screening to monitor overall well-being.
A CBC test can help diagnose conditions like anemia, infections, immune disorders, and certain cancers.
If you’re undergoing treatment for conditions like cancer or an infection, a CBC test helps monitor how your body responds to the treatment.
A CBC test is often required before surgery to ensure no underlying issues could complicate the procedure.
A CBC test may be ordered after surgery to assess recovery, especially in the context of infection or blood loss.

In most cases, no special preparation is needed for a CBC blood test. However, there are a few considerations:
Although a CBC test usually doesn’t require fasting, if it’s combined with other tests, such as a metabolic panel, your doctor may ask you to fast for several hours before the test.
Certain medications, such as steroids, antibiotics, and chemotherapy drugs, can influence your CBC results. The same is also true for several recreational and commonly abused substances. Be sure to inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking.
Hydration can impact the results of a CBC, as dehydration may cause a higher concentration of red blood cells. Avoid strenuous exercise before the test, as it can temporarily affect white blood cell levels.
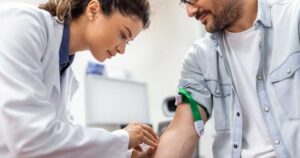
The CBC test procedure is simple and usually takes only a few minutes:
1. A healthcare provider will clean the area, typically the inside of your elbow, with antiseptic.
2. A needle is then inserted into a vein, and blood is drawn into a tube.
3. The blood sample is sent to the lab for analysis.

Understanding your CBC results can be daunting, but knowing the basic principles can make it easier to follow.
Low RBC, hemoglobin, or hematocrit
This may indicate anemia, which could be due to iron deficiency, blood loss, or chronic illness.
High WBC
A high white blood cell count often signals infection, inflammation, or even stress.
Low Platelet Count
This can point to conditions like thrombocytopenia, increasing the risk of bleeding.
High Platelet Count
This could indicate an underlying issue, such as a bone marrow disorder.
Some common conditions diagnosed through abnormal CBC results include:
While it’s possible to understand what your CBC results mean, only a healthcare provider can provide a complete interpretation based on your medical history, symptoms, and other tests.

While a Complete Blood Count (CBC) test is a safe and common procedure, like any medical test involving blood draws, it may come with minor risks and side effects. Here’s what you should be aware of:

The cost of a CBC test can vary depending on several factors.
On average, a CBC test in Portland, Oregon, costs between $30 and $100 without insurance. Prices may fluctuate based on where the test is performed and any additional fees for lab analysis.
Call Us ☎ at (503) 477-7748 to confirm exact pricing
Depending on your healthcare plan, insurance often covers a CBC test fully or partially. Out-of-pocket expenses can range from $0 to $30, depending on your deductible and co-pay.
Smart Labs Now offers convenient and affordable CBC and other blood tests in Portland, Oregon. If you’re a city resident or visitor, our goal is to empower you with quick, accurate, confidential, and budget-friendly medical testing options 🙂.
Check out our full range of affordable lab tests:

If you’re looking for a CBC blood test in Portland, Oregon, you have several options.

The tube used for a CBC test typically has a lavender top, which contains EDTA, an anticoagulant.
A comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) is often ordered alongside a CBC for a more detailed analysis of your overall health.
Automated machines analyze your blood sample in a laboratory to provide quick and accurate results.
Typically, about 2-5 mL of blood is needed for a CBC test.

The CBC blood test is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides critical information about your blood and overall health. Whether you’re undergoing a routine check-up, diagnosing a medical condition, or monitoring the effectiveness of a treatment, a CBC test can provide essential insights.
Regular health check-ups that include a CBC test are an excellent way to keep track of your health and catch potential issues early. Remember, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to interpret your results properly.
So, whether you’re preparing for surgery, managing a chronic condition, or just staying proactive about your health, a CBC blood test is a fundamental part of maintaining your well-being.
Please consult your primary care physician before engaging with any pharmaceutical, natural substances, or activity regimens mentioned or prescribed in this post. Smart Labs Now is not responsible for health or life outcomes based on the information or recommendations provided. This account does not serve as a substitute for professional medical advice/help.