
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2) is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that primarily causes genital herpes. Understanding HSV-2 test results can be challenging, especially when determining your next steps.
This guide explains who should get tested, how to prepare for the testing process, how to interpret results, and the available treatments.
We have a separate explainer on HSV-1 testing if you wish to learn more about it 🤓.
If you’re certain you have symptoms and want to get quick, affordable confirmation, schedule a test right away.

This article is for individuals considering HSV-2 testing, whether due to symptoms, exposure, or general concern about their sexual health. This includes those who have engaged in unprotected sex, experienced symptoms such as sores or blisters, or have been exposed to someone with genital herpes.

Before diving into the details of HSV-2 testing, it’s helpful to understand some relevant terms/concepts:
– HSV-2 infection: A viral infection caused by herpes simplex virus type 2, typically leading to genital sores.
– Contact: The virus spreads primarily through direct skin-to-skin contact, including sexual activity.
– Genital herpes: A condition resulting from HSV-2 infection, causing painful sores in the genital region.
– Genital secretions: Fluids from the genitals, including semen and vaginal discharge, that can carry the virus.
– Infections: The presence and multiplication of harmful microorganisms in the body.
– Lesions: Visible sores or ulcers, often a hallmark of herpes outbreaks.
– Mucosal surfaces: Moist tissues lining the body’s openings, such as the mouth and genitals, which are often affected by herpes infections.
– Oral secretions: Fluids from the mouth, such as saliva, which can also transmit the virus (though this is more common with HSV-1, which causes oral herpes).
– Testing: Undergoing a medical procedure to determine the presence of HSV-2.
– Transmission: Passing the virus from one person to another through sexual contact or other forms of skin-to-skin contact.
– Gender-Specific Complications: Both men and women are affected by HSV-2, but women may have unique concerns due to potential complications during pregnancy.

Understanding when to get tested for HSV-2 is crucial, as timing can affect the accuracy of your results. Below are key factors to consider:
If you notice signs of genital herpes, such as painful sores or blisters in the genital area, it’s important to get tested right away.
If you’ve had unprotected sex with someone who has HSV-2, you should consider testing within a few weeks. This allows time for the virus to trigger detectable antibodies in your bloodstream.
People with a history of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), a weakened immune system, or frequent unprotected sex should consider regular testing for HSV-2, even if they haven’t noticed symptoms.

Preparing for an HSV-2 test is straightforward, but here are a few things you might need to know:
Most HSV-2 tests do not require fasting, but depending on the type of test your healthcare provider recommends, some may have specific instructions.
A blood sample is required for an HSV-2 antibody test, so be prepared for a simple blood draw. This is our standard approach at Smart Labs Now for testing Herpes pathogens 🙂.
If active sores or blisters are present, your doctor may swab the affected area to test for the virus directly.
If sores are present in the genital area, partial undressing might be required for the test, but your healthcare provider will guide you through the process.
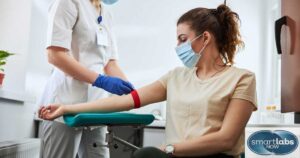
The two main types of HSV-2 tests are blood tests and viral cultures. The process is simple and usually quick:
A small blood sample is typically drawn from a vein in your arm.
The blood is analyzed for HSV-2 antibodies, which the body produces in response to infection.
If sores are present, a swab from the lesion can directly test for the presence of the virus.
Most results are available within a few days, depending on the lab processing time.

HSV-2 test results can fall into three categories—positive, negative, or indeterminate.
– Positive: If you test positive, it means you have been exposed to HSV-2 and your body has produced antibodies in response. It does not necessarily mean you are currently experiencing an outbreak.
– Negative: A negative result indicates no detectable HSV-2 antibodies in your system. However, if you were recently exposed, it’s important to note that it may be too early for the antibodies to develop, so you might need to be retested.
– Indeterminate: Sometimes, the results are unclear, indicating the need for a follow-up test. This could happen if the virus is in its early stages or due to other factors affecting the test’s accuracy.

If you receive a positive HSV-2 test result, taking the right steps is essential:
A healthcare provider can help you understand your results and explain your treatment options.
Prescription antiviral medications can manage symptoms and reduce the likelihood of outbreaks. These medications also lower the risk of transmitting the virus to others.
In some cases, your doctor may recommend additional tests to track the progression of the infection, particularly if you are pregnant or have other health concerns.

There’s currently no cure for HSV-2, but several antiviral medications can help manage the condition and reduce outbreaks:
– Acyclovir: A commonly prescribed antiviral that helps shorten outbreaks and reduces the frequency of recurrence.
– Valacyclovir: This antiviral works similarly to acyclovir but is often preferred because it requires fewer daily doses, making it easier to use.
– Famciclovir: “Another antiviral option for frequent outbreaks.”
While these treatments can control symptoms, they don’t eliminate the virus from your body. Practicing safe sex, using condoms, and avoiding sexual contact during outbreaks can help prevent spreading the infection.

Understanding HSV-2 test results can feel overwhelming, but you can take control of your health with the right information. If you suspect exposure to HSV-2 or experience symptoms, it’s important to get tested.
Consult your healthcare provider about your results, and work together to manage the condition with appropriate treatments and lifestyle modifications.
If you’re in Portland, trust us to unearth any Herpes infection you may be exposed to – discreetly, quickly, and affordably 🙂.
Please consult your primary care physician before engaging with any pharmaceutical, natural substances, or activity regimens mentioned or prescribed in this post. Smart Labs Now is not responsible for any health or life outcomes resulting from the use of the information or recommendations provided. This account does not serve as a substitute for professional medical advice.